Introduction
Who Owns Ferrari? It’s one of the most commonly asked questions among car addicts, luxury investors, and brand historians alike.The iconic Italian sports car maker isn’t the privately held company that Enzo Ferrari once ran behind the scenes. Instead, it’s a publicly traded global automotive brand with a unique ownership structure combining historic family investment and shareholders spread around the world.
In this article, we’ll take you beyond the surface to explain the ownership structure of Ferrari in 2026, how it changed over time, and why this matters — whether you’re investing, researching automotive history, or simply curious about one of the world’s most alluring car makers. We also include charts, summaries, and easy explanations to help both beginners and experts understand corporate ownership dynamics.
By the end of this model, you’ll know absolutely who controls the voting power, and how this control changes Ferrari’s future.
Ferrari at a glance:
| Attribute | Details |
| Founded | 1939 by Enzo Ferrari |
| Headquarters | Maranello, Italy |
| Ticker Symbol | RACE (NYSE & Euronext Milan) |
| Type | Publicly Traded Company |
| Largest Shareholder | Exor N.V. |
| Key Individual Owner | Piero Ferrari |
| CEO | Benedetto Vigna |
| Executive Chairman | John Elkann |
| Industry | Luxury sports cars & performance vehicles |
| Public Share Percentage | A major portion of shares is held publicly globally |
Company History & Ownership
Early Years: Enzo Ferrari Builds a Legend
Ferrari was founded in 1939 by Enzo Ferrari, originally in racing cars before building a road service starting in 1947. The company became a badge of the Italian system and attention.
The authorization Era
In 1969, Italian automaker Fiat S.p.A. purchased a 50% stake in Ferrari, helping greatly expand production and modern capacity. Over the next two decades, Fiat increased its stake up to 90%, while Enzo himself received the balance.
In spite of this investment, Ferrari maintained a distinct brand identity separate from common commodity products.
Spin-Off & IPO
Ferrari’s modern shift happened in 2015, when command Chrysler Automotive (FCA) spun off Ferrari into an independent publicly traded entity — Ferrari N.V. — and listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). Piero Ferrari, Enzo’s son, retained his share, while the rest of Ferrari’s stock was sold to public markets.
This move transformed Ferrari into a unique blend of heritage ownership and public investment, setting the stage for how ownership works today.
Ferrari Ownership Structure
Even though many people expect Ferrari to be privately owned by a family or Business, it is not fully private anymore. Instead, its shares are shared between:
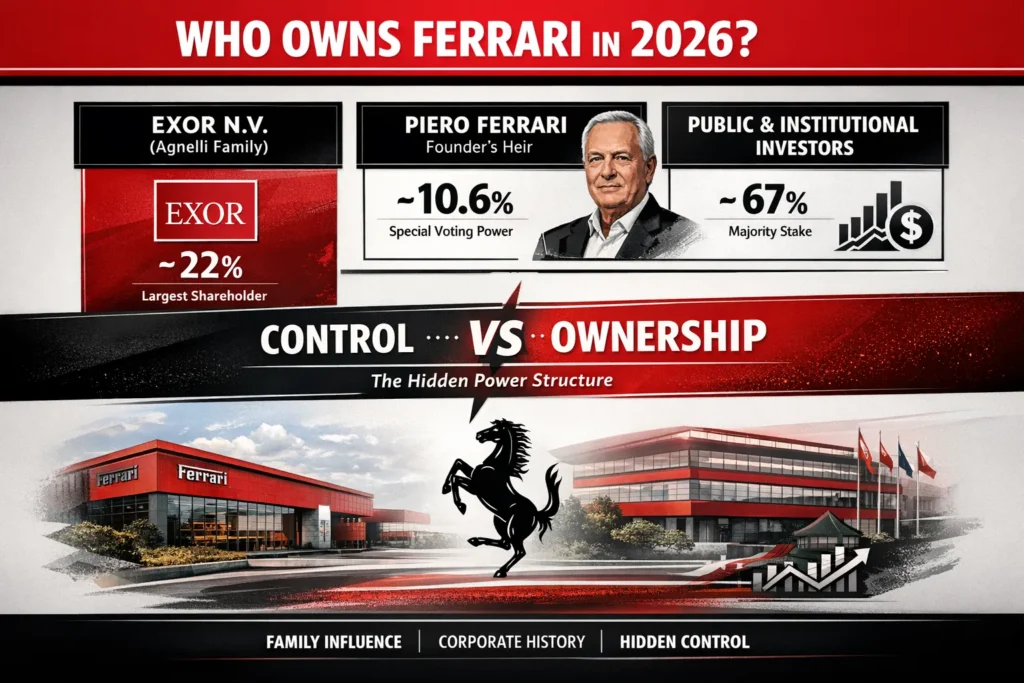
Exor N.V. – Largest investor
Exor N.V., the holding company of the Agnelli family, is Ferrari’s largest shareholder. As of March 2026:
- Equity Ownership: ~24.65%
- Voting Rights: ~36.48%
- Chairman: John Salt (Agnelli family heir)
Piero Ferrari – Founder’s Son
Piero Ferrari, Enzo Ferrari’s only surviving son, also owns a significant percentage of Ferrari’s shares:
- Equity Stake: ~10.48%
- Voting Power: ~15.51%
- Position: Vice Chairman of Ferrari
Public & Institutional
The remaining shares are held by public investors, including several major institutional investment groups.
- BlackRock
- Vanguard
- Groupama Asset Management
Collectively, public investors hold around 58–60% of Ferrari’s outstanding shares, although they don’t have as much Voting influence as Exor and Piero’s loyalty-linked shares.
Summary Ownership Chart
| Owner | Equity % | Voting Rights % |
| Exor N.V. | ~24.65% | ~36.48% |
| Piero Ferrari Trust | ~10.48% | ~15.51% |
| Public & Institutions | ~58.80% | ~48.01% |
| Other Minor Holders | Remainder | Remainder |
Why Ferrari’s Ownership Matters
Understanding who owns Ferrari isn’t just trivia — it affects:
● Strategic Vision
Exor and the Agnelli family help keep Ferrari’s long-term luxury and racing heritage intact.
● Innovation Decisions
Significant control by a minority shareholder means Ferrari can invest in future technologies without losing identity.
● Stock Market Moves
As a public company, Ferrari’s share price and investor sentiment affect capital raising and expansion.
How Ferrari Is Governed
Board of Directors
Ferrari’s board includes:
- John Elkann – Executive Chairman (Exor & Agnelli family)
- Piero Ferrari – Vice Chairman
- CEO: Benedetto Vigna
Governance balances heritage with modern business requirements, ensuring Ferrari stays competitive internationally.
Ferrari in the Public Markets
- Market demand for luxury and performance cars
- Growth in Asia & North America
- Brand collaborations and limited editions
- Motorsport success (especially in Formula 1)
What the Exor
In January 2026, Exor renewed its shareholder agreement with Piero Ferrari — confirming coordinated leadership and voting rights through 2029. This ensures stability and long-term strategic planning at Ferrari.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Long-term leadership continuity
- Balanced public investment and private heritage
- Strong global brand value
- Public shares provide financial flexibility
- Strategic shareholder agreements promote stability
Cons
- Minority public investors have limited control
- Exor’s decisions may prioritize a broader investment strategy
- A complex voting structure may be hard for beginners to grasp
- Shifts in large shareholders (e.g., institutional investors) can impact stock
- Public listing exposes Ferrari to market pressure
Who Should Understand Ferrari’s Ownership?
This topic is especially useful for:
- Investors evaluating Ferrari stock or similar luxury automakers
- Car enthusiasts curious about brand control
- Business and finance students learning about collective control
- History buffs hunting automotive estate brands
- Press and writers want exact, authentic information
FAQs
A: The founder’s son, Piero Ferrari, owns a powerful part and remains vice chairman.
A: Fiat (FCA) spun off Ferrari into its own public company in 2016.
A: Exor and Piero Ferrari control a significant portion of voting power through loyalty share mechanisms.
A: Its key leadership and largest shareholder remain Italian, while many global investors hold shares.
A: Public investors influence via markets, but major decisions are guided by strategy.
Conclusion
Today, Ferrari stands as more than a car company — it’s a design of performance, culture, and global luxury. Understanding who owns Ferrari helps reveal not just where the brand came from, but where it’s headed in the future. The company is honestly rotated, connecting historic leadership from the Agnelli family-controlled Exor and Ferrari with a broad public investor base that fuels global market Respect.











